.
P A Y W A L L E D S O U R C E : Nature
This is an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. Nature Research are providing this early version of the manuscript as a service to our authors and readers. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting and a proof review before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers apply.
Abstract
Short
telomere length is a risk factor for age-related disease, but it is also associated with reduced hippocampal volumes, age-related cognitive decline and psychiatric disorder risk. The current study explored whether
telomere shortening might have an influence on cognitive function and psychiatric disorder pathophysiology, via its hypothesised effects on adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
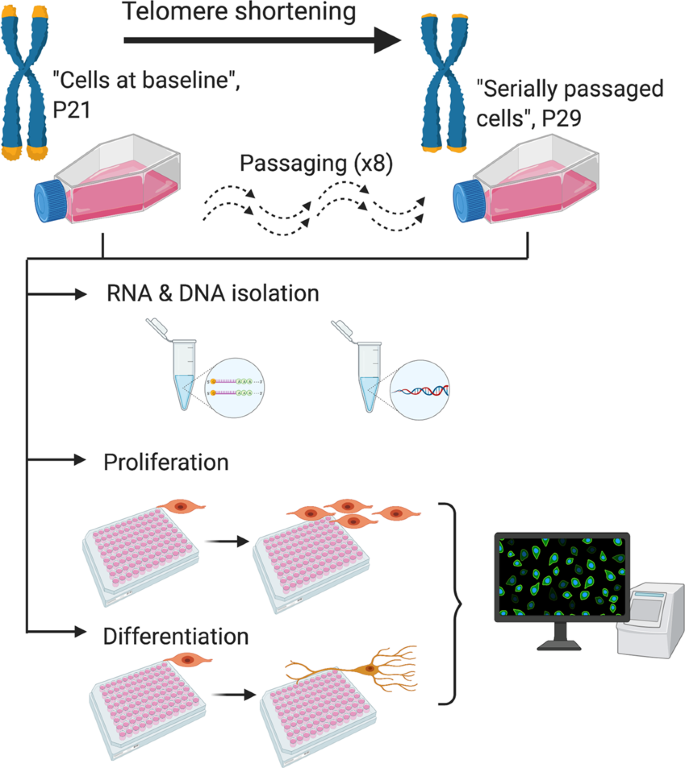
We modelled
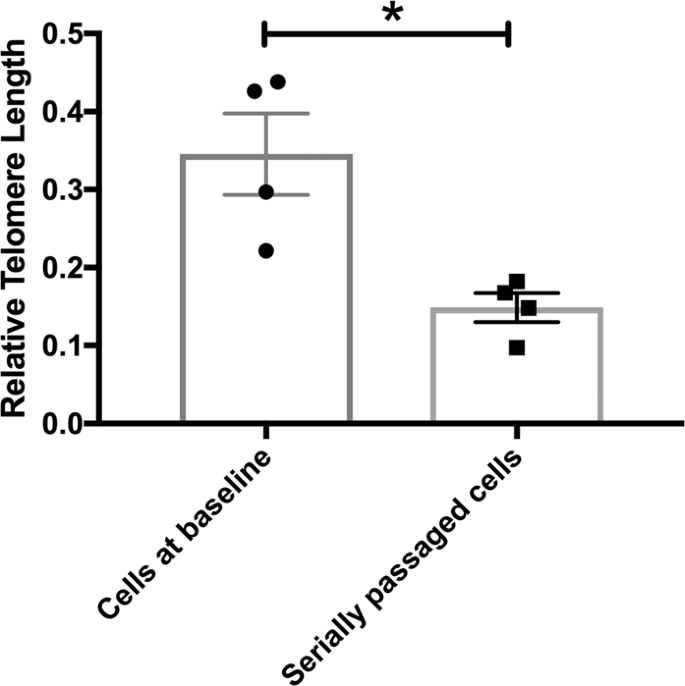
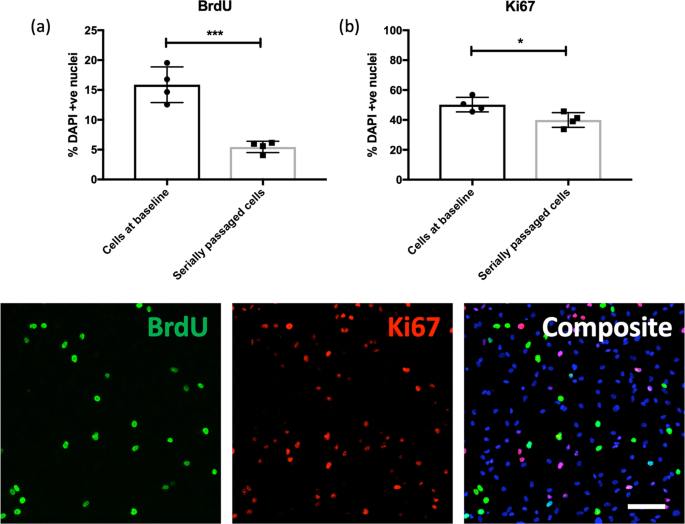
telomere shortening in human hippocampal progenitor cells in vitro using a serial passaging protocol that mimics the end-replication problem. Serially passaged progenitors demonstrated shorter
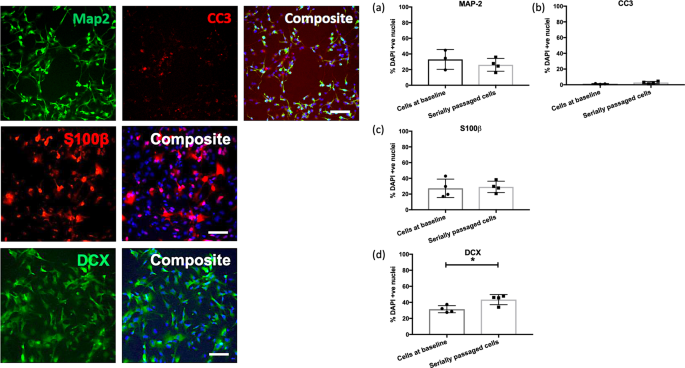
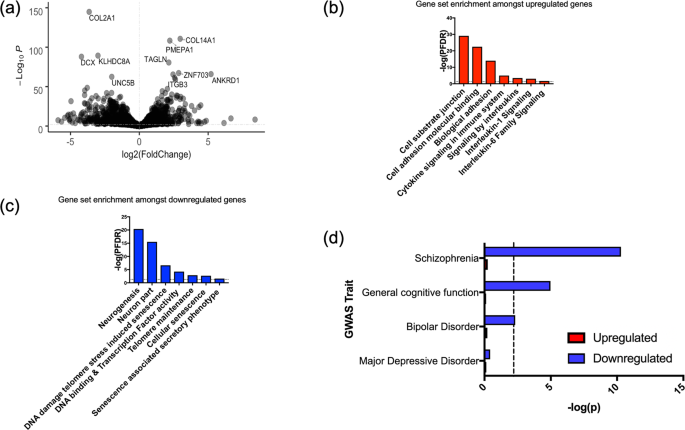
telomeres (P ≤ 0.05), and reduced rates of cell proliferation (P ≤ 0.001), with no changes in the ability of cells to differentiate into neurons or glia. RNA-sequencing and gene-set enrichment analyses revealed an effect of cell ageing on gene networks related to neurogenesis,
telomere maintenance, cell
senescence and cytokine production. Downregulated transcripts in our model showed a significant overlap with genes regulating cognitive function (P ≤ 1 × 10−5), and risk for schizophrenia (P ≤ 1 × 10−10) and bipolar disorder (P ≤ 0.005).
Collectively, our results suggest that
telomere shortening could represent a mechanism that moderates the proliferative capacity of human hippocampal progenitors, which may subsequently impact on human cognitive function and psychiatric disorder pathophysiology.
.