As rejuvenation research advances from theory to practice, more therapies start making their way into the clinic. 2025 continues with both mouse experiments and human clinical trials.
Interviews
 Cyclarity Launches Human Trial to Cure Atherosclerosis: Recently, Cyclarity Therapeutics announced the launch of a Phase 1 human clinical trial for a drug that aims to remove the arterial plaques that lead to heart attacks and strokes. Its primary cyclodextrin drug candidate, UDP-003, focuses on 7-ketocholesterol, a type of oxidized cholesterol that increases in cells and tissues as people age.
Cyclarity Launches Human Trial to Cure Atherosclerosis: Recently, Cyclarity Therapeutics announced the launch of a Phase 1 human clinical trial for a drug that aims to remove the arterial plaques that lead to heart attacks and strokes. Its primary cyclodextrin drug candidate, UDP-003, focuses on 7-ketocholesterol, a type of oxidized cholesterol that increases in cells and tissues as people age.
Marco Quarta on Cellular Senescence in Aging: Dr. Marco Quarta runs one of the most interesting start-ups in the longevity field: Rubedo, which focuses on utilizing the senolytic approach to cellular senescence. This company has developed ingenious ways to cope with the notorious heterogeneity of senescent cells and is one of the first to bring its senolytic drug candidate into clinical trials.
Advocacy and Analysis
The Battle for Long Life Has Been Accomplished: What’s Next?: How long can people live? This is not just a foundational question in science. The answer has important public policy implications and is of interest to us all. Recent scientific evidence has revealed the answer, so what’s next in humanity’s never-ending battle agai nst disease and the persistent ravages of aging?
nst disease and the persistent ravages of aging?
Research Roundup
Keeping Stem Cells Healthy and Young: A team of researchers has outlined a new approach that uses mRNA to prevent senescence and strengthen mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) against aging before they are transplanted into patients.
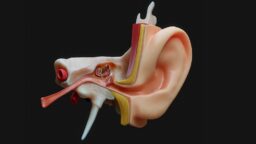 A Potential Gene Therapy for Hearing Loss: In JCI Insight, researchers have explored the possibility of using gene therapy to restore a crucial protein and repair hearing loss. The most critical finding is that the adult cochlea, which processes hearing, is in fact capable of being remodeled through changes in gene expression after birth.
A Potential Gene Therapy for Hearing Loss: In JCI Insight, researchers have explored the possibility of using gene therapy to restore a crucial protein and repair hearing loss. The most critical finding is that the adult cochlea, which processes hearing, is in fact capable of being remodeled through changes in gene expression after birth.
Drinking and Dying: Alcohol as a Risk Factor for Cancer: A new advisory by the US Surgeon General highlights a topic that – as the document itself notes – has been flying mostly under the public’s radar: the relationship between alcohol consumption and cancer.
 Receiving Caloric Restriction Benefits Without Practicing It: In a new study, researchers have found that lithocholic acid, a metabolite found in the serum of calorically restricted mice, can mimic the effects of caloric restriction. While their research was conducted on model systems, they point to a previous study that observed that this metabolte was observed to be increased in the serum of healthy humans following 36 hours of fasting.
Receiving Caloric Restriction Benefits Without Practicing It: In a new study, researchers have found that lithocholic acid, a metabolite found in the serum of calorically restricted mice, can mimic the effects of caloric restriction. While their research was conducted on model systems, they point to a previous study that observed that this metabolte was observed to be increased in the serum of healthy humans following 36 hours of fasting.
Precision Targeting of Senescent Cells: In a journal called Small, researchers have described a new targeting mechanism for delivering senolytic compounds where they need to go. These molecules are encapsulated in tiny soap bubbles rather than silica-based nanoparticles.
 Intermittent Fasting Improves Coordination in Mice: Researchers have discovered that intermittent fasting increases myelin in aged mice, leading to better neural function and coordination. Normally, neuronal axons are coated in a protein sheath made of myelin, which is necessary for their proper function, but demyelination occurs in aging.
Intermittent Fasting Improves Coordination in Mice: Researchers have discovered that intermittent fasting increases myelin in aged mice, leading to better neural function and coordination. Normally, neuronal axons are coated in a protein sheath made of myelin, which is necessary for their proper function, but demyelination occurs in aging.
A Gut Metabolite Reduces Senescence and Inflammation: In a preprint study, scientists from Lifespan Research Institute and the Buck Institute for Research on Aging have published their findings that Urolithin A, a molecule that has garnered a lot of attention in the longevity field, potently reduces senescence-related markers in human fibroblasts.
 The Impact of a Human Breast Milk Probiotic on Sarcopenia: The authors of this study, citing evidence of a link between the gut microbiome, muscle health, and sarcopenia, investigated the effect of the consumption of a probiotic on the muscle health of sarcopenia patients.
The Impact of a Human Breast Milk Probiotic on Sarcopenia: The authors of this study, citing evidence of a link between the gut microbiome, muscle health, and sarcopenia, investigated the effect of the consumption of a probiotic on the muscle health of sarcopenia patients.
Enhancing NAD+ Efficiency by Energizing Sirtuins: Researchers publishing in Physical Review X have discovered compounds that can double the efficiency of the sirtuin SIRT3 in processing NAD+. Unlike previous efforts, this drug does not rely on a substrate to function.
 New Study Links Epigenetic Changes to Genetic Mutations: A new paper published in Nature Aging suggests that somatic mutations cause significant remodeling of the epigenetic landscape. The findings might be relevant to future anti-aging interventions.
New Study Links Epigenetic Changes to Genetic Mutations: A new paper published in Nature Aging suggests that somatic mutations cause significant remodeling of the epigenetic landscape. The findings might be relevant to future anti-aging interventions.
Fighting Alzheimer’s by Helping Neurons Consume Proteins: Researchers have found that kinesin family member 9 (KIF9), a protein that diminishes with aging, is instrumental in allowing cells to consume harmful proteins and fights Alzheimer’s in a mouse model.
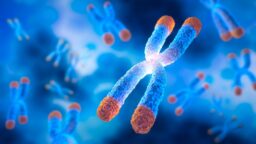 Maintaining Telomeres Extends Lifespan in Mice: A recent study has found that the overexpression of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), which is a subunit of telomerase, an enzyme essential for telomere maintenance, leads to lifespan extension in mice without significant side effects.
Maintaining Telomeres Extends Lifespan in Mice: A recent study has found that the overexpression of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), which is a subunit of telomerase, an enzyme essential for telomere maintenance, leads to lifespan extension in mice without significant side effects.
Maintaining Muscle by Restoring Gut Bacteria: In Aging Cell, researchers have described how different combinations of gut bacteria impact muscle strength in mice. The link between gut bacteria and health is well-documented, and multiple biomarkers have confirmed that a healthy gut leads to health elsewhere.
 New Drug Eliminates Breast Cancer in Mouse Study: Researchers have discovered a small molecule that effectively kills cancer cells in the most prevalent type of breast cancer. The new drug could help against cancer recurrence and decrease the need for surgery.
New Drug Eliminates Breast Cancer in Mouse Study: Researchers have discovered a small molecule that effectively kills cancer cells in the most prevalent type of breast cancer. The new drug could help against cancer recurrence and decrease the need for surgery.
Restoring Cellular Proliferation Through Exosomes: In Cell Metabolism, researchers have described how a microRNA (miRNA) derived from exosomes generated by human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) restores function and fights senescence in cell cultures and mice.
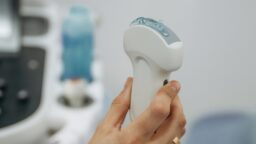 Ultrasound as a Tool to Eliminate Senescent Cells: A new study suggests that low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) can be beneficial in eliminating senescent cells through the recruitment and activation of immune cells. LIPUS is a technology that can be easily applied in the clinic.
Ultrasound as a Tool to Eliminate Senescent Cells: A new study suggests that low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) can be beneficial in eliminating senescent cells through the recruitment and activation of immune cells. LIPUS is a technology that can be easily applied in the clinic.
Inhibiting a Fundamental Factor in Brain Inflammation: Researchers have devised a method of reducing brain inflammation by creating a long-lasting inhibitor of the inflammatory factor NF-κB. These researchers believe that it “may serve as a potent therapeutic agent against pathological age-related inflammatory processes, especially those that target macrophages and microglia.”
 Artificially Grown Tissue Repairs Heart Failure in Monkeys: German scientists have created lab-grown “patches” of heart muscle tissue derived from pluripotent stem cells. Following a success with rhesus monkeys, they have obtained approval for a human trial.
Artificially Grown Tissue Repairs Heart Failure in Monkeys: German scientists have created lab-grown “patches” of heart muscle tissue derived from pluripotent stem cells. Following a success with rhesus monkeys, they have obtained approval for a human trial.
Reducing functionally defective old HSCs alleviates aging-related phenotypes in old recipient mice: This study demonstrates the presence of “younger” HSCs in old mice and that aging-associated functional decline can be mitigated by reducing dysfunctional HSCs.
Tenascin-C promotes bone regeneration via inflammatory macrophages: Taken together, this study reveals the regulation of macrophage recruitment and its function in the activation of skeletal stem cells after bone injury, providing a strategy to accelerate bone regeneration by TNC delivery.
Innovative treatment of age-related hearing loss using MSCs and EVs with Apelin: These findings highlight the regenerative capabilities of MSCs and EV-mediated therapeutic approaches for this condition.
Delivery of FGF18 using mRNA-LNP protects the cartilage against degeneration via alleviating chondrocyte senescence: In summary, this study presents a novel approach superior to recombinant protein alone and holds promise as a new therapeutic strategy for OA.
Data-driven discovery of associations between prescribed drugs and dementia risk: A systematic review: Drug repurposing for use in dementia is an urgent priority. These findings offer a basis for prioritizing candidates and exploring underlying mechanisms.
Intestine-specific disruption of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase extends longevity: Combined, these results indicate that disruption of sod-2 in neurons, intestine, germline, or muscle is not required for lifespan extension, but that decreasing sod-2 expression in just the intestine extends lifespan.
Protection of Alzheimer’s disease progression by a human-origin probiotics cocktail: These results suggest that this unique probiotics cocktail could serve as a prophylactic agent to reduce the progression of cognitive decline and AD pathology.
The role of the Mediterranean diet in reducing the risk of cognitive impairement, dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis: These findings underscore the Mediterranean diet’s potential as a central element in neuroprotective public health strategies to mitigate the global impact of cognitive decline and dementia and to promote healthier cognitive aging.
Dietary carotenoid intakes and biological aging among US adults, NHANES 1999–2018: Increased dietary intakes of various carotenoids were associated with lower biological aging indices, which was possibly and mainly driven by lutein/zeaxanthin and β-carotene.
Multi-omics characterization of improved cognitive functions in Parkinson’s disease patients after the combined metabolic activator treatment: These results show that combined metabolic activator administration leads to enhanced cognitive function and improved metabolic health in Parkinson’s disease patients as recently shown in Alzheimer’s disease patients.
Combination of rapamycin and adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells enhances therapeutic potential for osteoarthritis: These findings suggest that the rapamycin and AD-MSC combination enhances the therapeutic efficacy of these cells in senescence-driven degenerative diseases such as OA, notably by improving their anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Long-term intake of Tamogi-take mushroom (Pleurotus cornucopiae) mitigates age-related cardiovascular dysfunction and extends healthy life expectancy: Ingestion of Tamogi-take mushrooms could serve as a dietary intervention to promote cardiovascular health, support healthy aging and slow the progression of age-related diseases.
Ergothioneine improves healthspan of aged animals by enhancing cGPDH activity through CSE-dependent persulfidation: These findings elucidate this compound’s multifaceted actions and provide insights into its therapeutic potential for combating age-related muscle decline and metabolic perturbations.
Comprehensive evaluation of lifespan-extending molecules in C. elegans: These findings confirmed robust lifespan extension by many, but not all, of the 16 tested compounds from the literature and revealed that some of them could be combined to obtain additive effects.
Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, c-Myc (OSKM) gene therapy in the hypothalamus prolongs fertility and ovulation in female rats: Long-term OSKM gene therapy in the hypothalamus is able to extend the functionality of such a complex system as the hypothalamo-pituitary-ovarian axis.
Transcriptomic signatures and network-based methods uncover new senescent cell anti-apoptotic pathways and senolytics: Identifying new antiapoptotic resistance targets and drugs with potential senolytic activity paves the way for developing new pharmacological therapies to eliminate senescent cells selectively.
NAD World 3.0: the importance of the NMN transporter and eNAMPT in mammalian aging and longevity control: This approach features multi-layered feedback loops to provide a more comprehensive understanding of NAD.
Activation of Nuclear Receptor CAR: A Pathway to Delay Aging through Enhanced Capacity for Xenobiotic Resistance: These results suggest that the longevity effects of CAR agonists may be related to the enhancement of xenobiotic resistance of animals.
Long-Term Impact of Using Mobile Phones and Playing Computer Games on the Brain Structure and the Risk of Neurodegenerative Diseases: Lengthy mobile phone use is associated with a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases and improved brain structure compared to minimal usage.
News Nuggets
 Vitalia Co-Founders Announce Split-up: Vitalia co-founders Niklas Anzinger and Laurence Ion today announced that they will be leading two new, separate organizations, Viva City and Infinita City. “Together, we built Vitalia from the ground up, establishing a foundation that has led us to this exciting new chapter,” said Anzinger and Ion in a joint statement.
Vitalia Co-Founders Announce Split-up: Vitalia co-founders Niklas Anzinger and Laurence Ion today announced that they will be leading two new, separate organizations, Viva City and Infinita City. “Together, we built Vitalia from the ground up, establishing a foundation that has led us to this exciting new chapter,” said Anzinger and Ion in a joint statement.
Cyclarity Launches Human Trial for Atherosclerosis: Cyclarity Therapeutics, a biotechnology company based at the Buck Institute in California, has launched its first human clinical trial. Its primary candidate cyclodextrin drug, UDP-003, focuses on 7-ketocholesterol, an oxidized cholesterol variant that builds up in cells as we age.
 Cutting-Edge Facility Expands to Support Cancer Therapy: New York Gov. Kathy Hochul and leaders from The Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center came together on Monday to celebrate the opening of the newly expanded Roswell Park Good Manufacturing Engineering and Cell Manufacturing Facility (GMP).
Cutting-Edge Facility Expands to Support Cancer Therapy: New York Gov. Kathy Hochul and leaders from The Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center came together on Monday to celebrate the opening of the newly expanded Roswell Park Good Manufacturing Engineering and Cell Manufacturing Facility (GMP).
New Database Lets You Know How Processed Your Food Is: Scientists have presented GroceryDB, an open-access online database that measures the degree of processing of tens of thousands of products sold in three major US grocery chains.
Coming Up
 Founders Longevity Forum and NUS Announce Event: Founders Longevity Forum Singapore, hosted in collaboration with the National University of Singapore (NUS) Academy for Healthy Longevity, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, and Longevity.Technology is set to host a pivotal two-day event on 27-28 February 2025, in Singapore.
Founders Longevity Forum and NUS Announce Event: Founders Longevity Forum Singapore, hosted in collaboration with the National University of Singapore (NUS) Academy for Healthy Longevity, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, and Longevity.Technology is set to host a pivotal two-day event on 27-28 February 2025, in Singapore.
The Global Conference on Gerophysics: Chaired by Prof Brian Kennedy, Assoc Prof Jan Gruber and Dr Maximilian Unfried, this pioneering conference will bring together leading theoretical physicists and eminent researchers in ageing and rejuvenation biology to explore a transformative new field: ‘Gerophysics’.
 The 3rd Longevity Med Summit Heads to Lisbon in May 2025: The Global 3rd Longevity Med Summit, the premier global event in longevity medicine, wellness, and healthcare innovation, is set to take place in Lisbon from May 6 to 8, 2025. This year’s summit promises an expanded agenda featuring groundbreaking topics, world-renowned speakers, and an exclusive Pre-Summit Day focused on the Future of Wellness.
The 3rd Longevity Med Summit Heads to Lisbon in May 2025: The Global 3rd Longevity Med Summit, the premier global event in longevity medicine, wellness, and healthcare innovation, is set to take place in Lisbon from May 6 to 8, 2025. This year’s summit promises an expanded agenda featuring groundbreaking topics, world-renowned speakers, and an exclusive Pre-Summit Day focused on the Future of Wellness.
Hevolution Foundation Hosts Second Global Healthspan Summit: On February 4-5, 2025, Hevolution Foundation will hold its second Global Healthspan Summit (GHS) in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The two-day event at the Four Seasons Hotel brings together international attendees, including world leaders, policymakers, researchers & scientists, and experts from the biotechnology, pharmaceutical, healthcare, and private sectors.








































