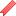
Parp-1 activity is reduced by AMPK activation. Telmisartan, Metformin and AICAR elicit this metabolic cascade. Metoprolol, glipizide does not.
Cardiovascular Protective Effect of Metformin and Telmisartan: Reduction of PARP1 Activity via the AMPK-PARP1 Cascade.
Hyperglycemia and hypertension impair endothelial function in part through oxidative stress-activated poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1). Biguanides and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) such as metformin and telmisartan have a vascular protective effect. We used cultured vascular endothelial cells (ECs), diabetic and hypertensive rodent models, and AMPKα2-knockout mice to investigate whether metformin and telmisartan have a beneficial effect on the endothelium via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation of PARP1 and thus inhibition of PARP1 activity. The results showed that metformin and telmisartan, but not glipizide and metoprolol, activated AMPK, which phosphorylated PARP1 Ser-177 in cultured ECs and the vascular wall of rodent models. Experiments using phosphorylated/de-phosphorylated PARP1 mutants show that AMPK phosphorylation of PARP1 leads to decreased PARP1 activity and attenuated protein poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation (PARylation), but increased endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity and silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 1 (SIRT1) expression. Taken together, the data presented here suggest biguanides and ARBs have a beneficial effect on the vasculature by the cascade of AMPK phosphorylation of PARP1 to inhibit PARP1 activity and protein PARylation in ECs, thereby mitigating endothelial dysfunction.

Western blot analysis of AMPK Thr-172 and PARP1 Ser-177 phosphorylation in HUVECs treated with concentrations of metformin (A), glipizide (B), telmisartan ©, and metoprolol (D) for 4 hr or (E-H) metformin (5 mM), glipizide (500 nM), telmisartan (5 μM), and metoprolol (500 μM) for the indicated times. Data are mean±SD ratio of phospho-PARP1 to total PARP1 and phospho-AMPK to total AMPK from 3 independent experiments. *p<0.05 compared to controls.

Twelve week-old male C57BL6 mice were administered (A) metformin (200 mg/kg body weight), (B) glipizide (1.3 mg/kg body weight), © telmisartan (10 mg/kg body weight), or (D) metoprolol (30 mg/kg body weight) for the indicated times. Control mice received 0.5 ml saline. Western blot analysis of AMPK and PARP1 phosphorylation in aortic extracts from 2 mice pooled. Data are mean ± SD ratio of phospho-PARP1 to total PARP1 and phospho-AMPK to total AMPK (n = 8 mice per group). *p<0.05 compared to controls.
Edited by prophets, 10 August 2016 - 03:18 PM.
































 This topic is locked
This topic is locked